|
Tutorial 5
1:45 – 5:30pm, Monday,
September 2009
MODELLING OF HYBRID ELECTRIC
VEHICLES FOR ENERGY MANAGEMENT
in the framework of
MEGEVH, French network on HEVs
Professor
Alain BOUSCAYROL
MEGEVH, French
network on HEVs
https://l2ep.univ-lille1.fr/megevh/
University of Lille 1, Sciences
et Technologies, L2EP
https://l2ep.univ-lille1.fr/
Hybrid Electric Vehicles are more and more
developed to face the problems of green house gases and
petroleum resource depletion. A lot of HEV topologies have
been developed in the last decade [1]-[3]. Energy management
is a key issue of HEV development in order to enable HEVs to
be competitive with thermal vehicles despite their cost. But
the modeling of such systems is quite complex because of the
multi-physical interconnected subsystems and the multi-scale
dimension of the different dynamics [4]. A cybernetic approach
is required to take into account dynamic
interaction of these multi-physical systems.
Different approaches have been used to model HEVs for energy
management: quasi-static or dynamic modeling [5], forwards or
backward methods, causal or non-causal models…
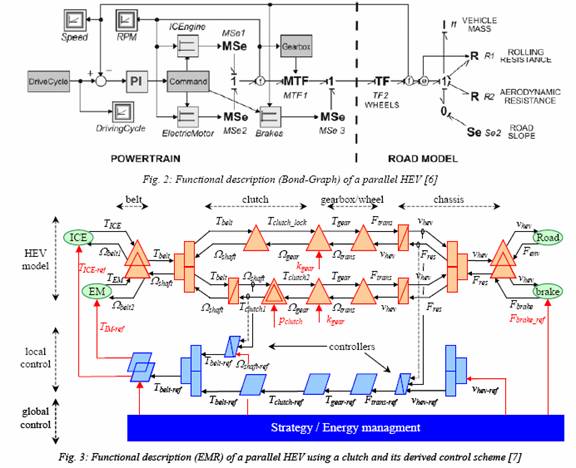
More recently graphical descriptions, such as
Bond Graph [6] or Energetic Macroscopic Representation [7],
have been introduced to help users by highlighting energy
properties and power flow constraints of the HEV topologies.
The aim of this tutorial is to present different modeling
methods for HEV energy management. Requirements of HEV
modeling and energy management will be
discussed. An example of a series parallel HEV will be studied
using Energetic Macroscopic Representation.

The tutorial is composed of two parts. The
first part will be dedicated to the different modeling methods
for energy management of complex systems:
·
Structural and functional
description,
·
Backwards and forwards approach,
·
Causal and non-causal modeling,
·
Different modeling objectives,
·
Graphical descriptions,
·
Requirements for energy
management of HEVs
The second part will be focused on the study of
a series-hybrid HEVs. Energetic Macroscopic Representations (EMR)
is chosen as example of graphical description for the
development of energy management:
·
Structural description of the
studied HEV,
·
Functional description of the
studied HEV using EMR,
·
Analysis of the possible energy
management from its EMR,
·
Control scheme of the studied HEV
derived from its EMR,
·
Energy management of the studied
EMR,
·
Simulation and experimental
results,
·
Extension to other HEVs
Biography: Alain BOUSCAYROL
received Ph.D. degree in Electrical Engineering
from INP Toulouse, France, in 1995. He was engaged as
assistant Professor at University of Lille 1, Sciences and
Technologies, France in 1996. He received the "Habilitation ŕ
Diriger des Recherches" degree from the University of Lille 1
in 2003. He has been engaged as Professor at University of
Lille 1 since 2005. From 1998 to 2004, he managed the
Multi-machine Multi-converter Systems project of GdR-ME2MS, a
national research program of CNRS (French National Centre of
Scientific Research). Since 2004, he has managed the national
network on Energy Management of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (MEGEVH).
He will be General Chair of IEEE VPPC 2010, Lille, France. His
research interests at the L2EP (Laboratory of Electrical
Engineering of Lille) include graphical descriptions
(Energetic Macroscopic Representation...) for control of
electric drives, wind energy conversion systems, railway
traction systems, electric and hybrid vehicles. His
collaborative works with industry on energy management for
vehicles include Siemens Transportation Systems, PSA Peugeot
Citroen and Valeo.
|