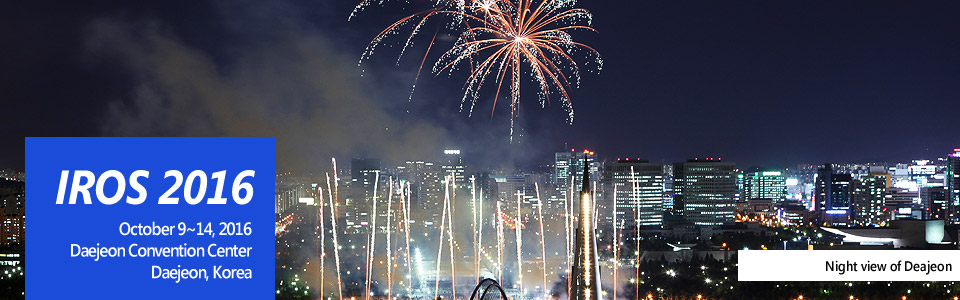IROS 2016 Organizing Committee is pleased to offer a range of technical tours. The technical tour application (and payment) should be done during the on-line registration process on the website. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
All submissions will undergo a common review process in Organizing Committee. Decisions about acceptance will be based on the potential significance, the sustainability in IROS’s, and the accommodation capability. All the submissions are made in email to sec@iros2016.org with the title of “Proposal to IROS2016 Competitions: your name”. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
ROBOTWORLD is one of the three biggest international robot shows, which consists of exhibition, contest, and conference all-in-one. This is especially driven by the Korean government since 2006 to boost industry as a whole, which had been at its fledgling stage of development. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The KI building embodies KAIST's commitment to presenting a new model of creative and interdisciplinary research and to becoming a globally-competitive research-oriented university. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dr. M is a networked medical service system provided through the Internet of Things (IoC), wearable electronics, smart home, and smart car. Under this care, people can monitor their health on a daily basis at any-time and place, helping them to lower the risk of serious health problems. Patients who have chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular illness can inform doctors of their health status in real time. Moreover, people living in remote regions can receive quality medical services without traveling long distances. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
The KAIST Institute (KI) was established in 2006 to foster interdisciplinary research at KAIST. The KI Building, which has become a landmark at KAIST, was completed in 2010. Robotics Lab was newly formed in 2016 as one of the KI's 6 labs to make an impact on the emerging technology through intelligent robots with interdisciplinary research effort. The Lab. has roots in several research topics: Humanoid Robot, Artificial intelligence, Perception & Mobility, Task-oriented robots, and Affective computing. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
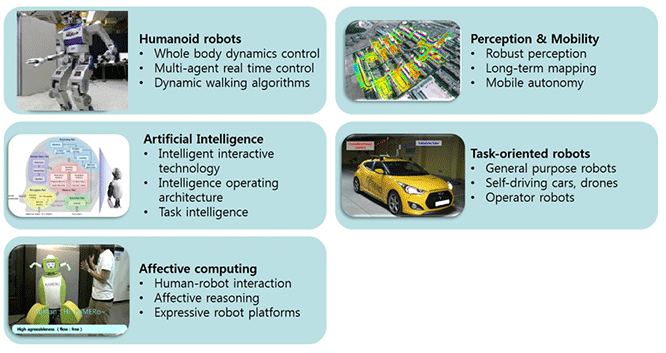
KAIST's humanoid robot, HUBO, was originally created by Jun-Ho Oh, a professor of the department of mechanical engineering, in 2004. Since then, the robot has gone through technological advancements. So far, more than 20 HUBOs have been exported for further studies in robotics to universities, research institutes, and private companies in the US, China, and Singapore. It is well known that the latest version of HUBO named DRC-HUBO won the Darpa Robotics Challenge in the first place with $2 million of prize money. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Human-Robot Interaction Research Center(HRI-RC) at KAIST was established in 2004 by Prof. Dong-Soo Kwon and the objective of the HRI-RC lies on the development of human-robot interaction technology for the promotion of welfare in human’s daily life and the creation of the business model with core HRI technologies. Major research area of HRI-RC includes human-robot interaction interfaces, medical robot and haptics. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
HRI researches have many issues in the field of perception, cognition, emotional interaction, and expression. At the first stage, a HRI architecture was developed to provide a robot’s interface capability which can make robots understand the users’ natural command, and execute the given tasks correctly. The developed multi-modality-based perception module consists of human detection, face/voice/gesture/emotion recognition. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
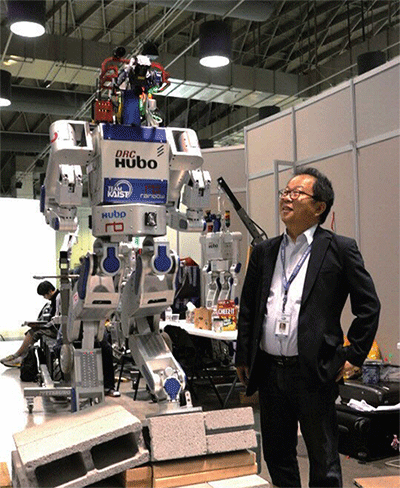
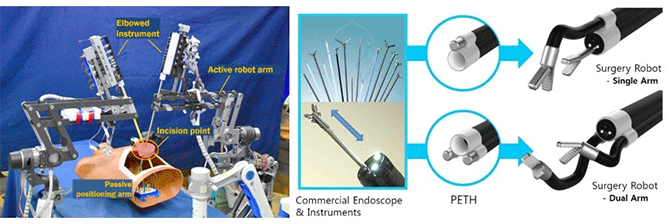
Our medical group research has been focusing on developing surgery robots, aiming to minimize invasiveness for patients, and maximize convenience for surgeons. Currently three major surgical robot systems have been developed in this context. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Haptics is a research field that creates sense of touch in terms of forces and tactile feedback. It can be used to assist in the creation of virtual objects in a computer simulation, to control virtual objects, and to enhance the remote control of machines and devices. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
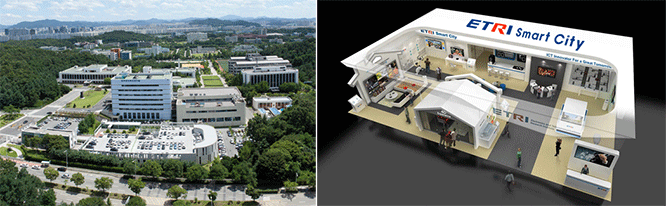
Since its foundation in 1976, ETRI, a global ICT research institute, has been making its immense effort to provide Korea a remarkable growth in the field of ICT industry. ETRI delivers Korea as one of the top ICT nations in the World, by unceasingly developing world’s first and best technologies. The main functions of ETRI are creation, development and dissemination of knowledge and technology required for the development in the field of information, telecommunications, electronics, broadcasting and related convergence technology. Main representative research areas are IT convergence technology, software, components & materials, broadcasting & telecommunications media, communications & internet, and technology commercialization division. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Designed in 1973, DAEDEOK science town had been the oldest and largest government-funded science complex in Korea. Today, 70 R&D institutes (including 30 government sponsored institutes), 6 universities, and over 800 companies in advanced fields of IT, BT, NT, ST and RT have formed a next generation innovation cluster in Daedeok. With over 14,000 researchers and more than 10% of all Korean patents, Daedeok has a proven track record in the commercialization of DRAM, SRAM, LCD modules, CDMA and wireless broadband technologies. They’re also well known for the development of the blockbuster drug ‘Factive’ and for developing an AIDS diagnostic test, WiBro (Wireless Broadband), DMB (Digital Multimedia Broadcasting), and launching 10 cutting-edge satellites. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Founded in 1976, the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) is a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning. KIMM's mission is to contribute to economic growth of the nation by performing research & development (R&D) on key technologies in the area of mechanical engineering. KIMM conducts reliability tests, evaluates machine components and materials, and commercializes the developed products or machineries through technology transfer and support. KIMM's research interests are widely spread from the nano-scale to macroscale and cover five research divisions; Advanced Manufacturing Systems, Nano-Convergence Mechanical Systems, Environment and Energy Systems, Extreme Mechanical Systems Engineering, and Mechanical Systems Safety. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||

Technical Tour